How Schools Can Support Positive Mental Health in Students
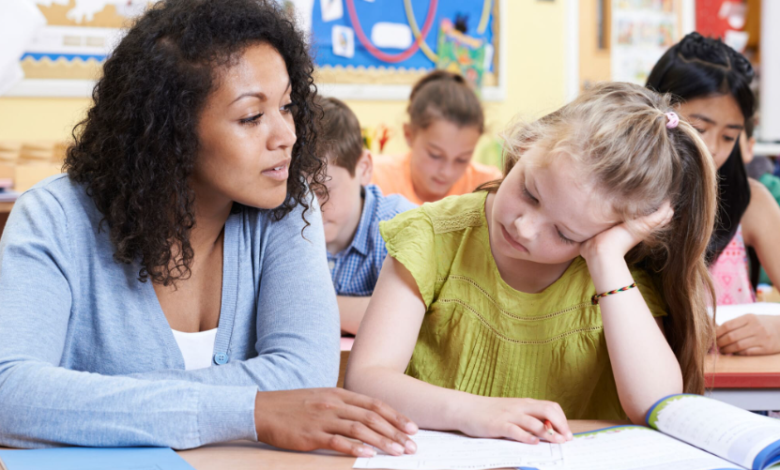

The school environment plays a pivotal role in the holistic development of young people, extending far beyond academic achievement. In an era where mental health challenges among students are increasingly prevalent, schools are uniquely positioned to foster resilience, promote well-being, and provide crucial support. From academic pressures to social dynamics and personal struggles, students face a myriad of factors that can impact their mental health. Recognizing and addressing these issues proactively is not just a moral imperative but a foundational element for creating a thriving educational community. This article explores practical strategies and systemic approaches schools can adopt to cultivate a supportive environment for student mental health, helping them navigate challenges and build a strong foundation for their future.
Understanding the Landscape: Why Student Mental Health Matters
The statistics paint a stark picture: a significant percentage of young people experience mental health conditions, with many symptoms emerging during adolescence. Conditions like anxiety and depression can profoundly affect a student’s ability to learn, socialize, and engage with their environment. Untreated mental health issues can lead to academic decline, social isolation, behavioral problems, and, in severe cases, more serious and long-lasting consequences. Schools are often the first place where signs of distress are observed, making them critical touchpoints for early intervention and support.
Creating a mentally healthy school environment isn’t solely about crisis intervention; it’s about building a culture where well-being is prioritized, stigma is reduced, and students feel safe to seek help. This involves a multi-faceted approach that integrates mental health support into the very fabric of the school day.
Proactive Strategies for Fostering Well-being
1. Cultivating a Supportive and Inclusive School Culture
A positive school culture is the bedrock of student mental health. This involves:
- Promoting Empathy and Respect: Educators and staff should model and teach empathy, respect, and kindness. Anti-bullying programs, diversity initiatives, and restorative justice practices can help create an environment where all students feel valued and accepted.
- Encouraging Open Communication: Foster an atmosphere where students feel comfortable discussing their feelings and concerns without fear of judgment. This can be achieved through regular check-ins, anonymous suggestion boxes, and designated “safe spaces.”
- Building Strong Relationships: Encourage strong student-teacher relationships and peer connections. Mentorship programs, collaborative projects, and extracurricular activities can help students build a sense of belonging and community.
2. Integrating Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) into the Curriculum
SEL focuses on developing self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making. Incorporating SEL into daily lessons can equip students with essential life skills:
- Mindfulness and Stress Reduction Techniques: Teach students practical strategies like deep breathing, meditation, and progressive muscle relaxation to manage stress and anxiety. Regular “mindfulness moments” can be integrated into the school day.
- Emotional Regulation Skills: Help students identify and understand their emotions, and provide them with constructive ways to express and manage them. Role-playing scenarios can be particularly effective.
- Conflict Resolution and Communication Skills: Equip students with the tools to resolve disagreements peacefully and communicate effectively, fostering healthier relationships.
3. Enhancing Staff Training and Awareness
For schools to effectively support student mental health, their staff must be adequately prepared:
- Professional Development in Mental Health First Aid: Train teachers, administrators, and support staff to recognize the signs of mental health distress and how to respond appropriately. This includes knowing when and how to refer students to professional help.
- Understanding Trauma-Informed Practices: Many students may have experienced trauma. Training staff in trauma-informed approaches helps them understand the impact of trauma on behavior and learning, allowing for more empathetic and effective responses.
- Burnout Prevention for Staff: Staff well-being is crucial. Schools should also provide resources and support to help their employees manage stress and prevent burnout, as a healthy staff is better equipped to support students.
See also: How Cloud Technology Supports Online Education
Responsive Measures: Providing Targeted Support
1. Accessible Mental Health Services
Schools should strive to make mental health support readily available:
- On-Site Counseling and Therapy: Providing access to qualified school psychologists, counselors, and social workers can ensure students receive timely support. These professionals can offer individual counseling, group therapy, and crisis intervention.
- Partnerships with Community Mental Health Providers: Establish strong relationships with local mental health organizations to facilitate seamless referrals for specialized services, including comprehensive anxiety disorder treatment. This ensures students who require more intensive care can access it.
- Clear Referral Pathways: Develop a clear, confidential process for students, parents, or staff to refer concerns about a student’s mental health. This pathway should be well-communicated and easy to navigate.
2. Early Identification and Intervention
Catching mental health issues early can prevent them from escalating:
- Regular Mental Health Screenings: Implement non-invasive, age-appropriate mental health screenings to identify students who may be at risk. These screenings should be conducted with parental consent and followed by appropriate action.
- Behavioral Observation and Communication: Train staff to observe subtle changes in student behavior or academic performance that could indicate a mental health challenge. Open communication channels between teachers, parents, and support staff are vital.
- Support Groups: Offer peer support groups for students facing common challenges, such as grief, anxiety, or family issues. This can provide a sense of community and shared experience.
3. Parent and Family Engagement
Parents are essential partners in supporting student mental health:
- Educational Workshops: Host workshops for parents on topics like recognizing signs of mental health issues, promoting resilience at home, and understanding anxiety disorder treatment options.
- Open Communication Channels: Maintain open and consistent communication with parents about their child’s well-being and academic progress.
- Resource Sharing: Provide parents with information about community mental health resources and support networks.
Conclusion
Creating a school environment that genuinely supports positive student mental health is a continuous journey, not a destination. It requires a comprehensive, multi-layered approach that integrates well-being into every aspect of school life. By prioritizing a supportive culture, embedding social-emotional learning, equipping staff with essential skills, and providing accessible mental health services, schools can become powerful catalysts for student resilience and growth. When students feel safe, supported, and understood, they are better equipped to learn, thrive, and develop into well-adjusted individuals. Investing in student mental health is an investment in their future, ensuring they have the tools to navigate life’s challenges and reach their full potential. This commitment also includes ensuring that effective anxiety disorder treatment and other mental health resources are readily available and understood within the school community.